How Might Climate Change Affect Future Global Migration?
Climate change is a pressing issue that continues to shape our world in profound ways. One significant aspect of this complex phenomenon is its potential impact on global migration patterns. As our climate evolves, so too may the movement of populations around the world. Understanding how climate change might influence future global migration is crucial for policymakers, researchers, and communities alike.
The Link Between Climate Change and Migration
Climate change is expected to bring about a range of environmental challenges, including rising sea levels, more frequent and severe natural disasters, and shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns. These changes can have far-reaching implications for communities across the globe, affecting everything from food security to access to clean water. In the face of such challenges, many people may be forced to leave their homes in search of safer and more sustainable living conditions. This connection between climate change and migration is complex and multifaceted, influenced by a variety of social, economic, and political factors.
Environmental Displacement: Forced Migration Due to Climate Change
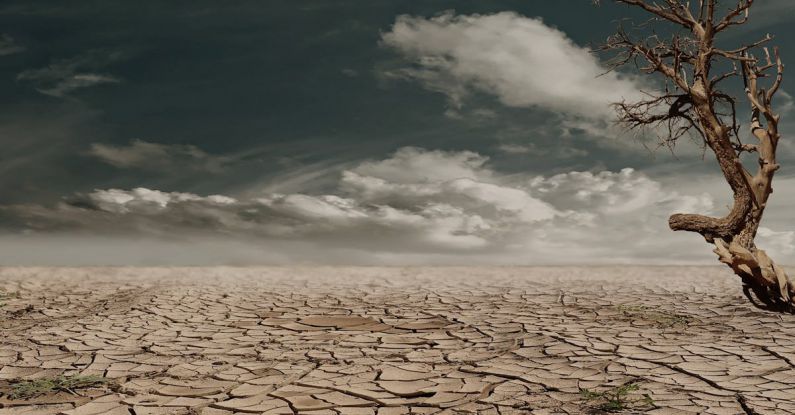
One of the most direct ways in which climate change is expected to impact global migration is through environmental displacement. As sea levels rise and extreme weather events become more frequent, low-lying coastal areas and vulnerable communities are at increased risk of displacement. Small island nations, such as Kiribati and the Maldives, are already facing the prospect of having to relocate their entire populations due to the threat of sea-level rise. In other regions, prolonged droughts and crop failures can lead to food insecurity and drive people to seek refuge elsewhere. This form of forced migration due to climate change poses significant challenges for both the affected populations and the countries they may seek to resettle in.
Conflict and Migration: The Role of Climate Change
In addition to directly displacing populations, climate change can also exacerbate existing social tensions and contribute to conflict, which in turn can drive migration. Competition for dwindling resources, such as water and arable land, may intensify in a changing climate, leading to conflicts within and between communities. In regions already grappling with political instability or social unrest, the added pressure of climate change can further destabilize populations and push them to migrate in search of safety and security. Understanding the interplay between climate change, conflict, and migration is essential for addressing the complex challenges that lie ahead.
Adaptation and Resilience: Building Sustainable Communities
While the potential impacts of climate change on global migration are significant, there are also opportunities to mitigate these challenges through adaptation and resilience-building efforts. Investing in sustainable infrastructure, disaster preparedness, and community-based solutions can help to reduce the risk of displacement and provide support to those who are forced to move. By addressing the root causes of environmental vulnerability and promoting sustainable development practices, we can work towards creating more resilient communities that are better equipped to withstand the impacts of a changing climate.
The Way Forward: Collaborative Solutions for a Changing World
As we look to the future, it is clear that climate change will continue to shape global migration patterns in profound ways. Addressing the complex challenges posed by environmental displacement, conflict, and societal resilience will require collaborative efforts at the local, national, and international levels. By working together to develop innovative solutions, build inclusive policies, and support vulnerable communities, we can create a more sustainable and equitable future for all. Climate change is a global issue that demands a coordinated and proactive response, and understanding its potential impact on future global migration is a critical step towards building a more resilient and adaptive world.